These days, Ansible is a big buzzword in the IT industry. It is a radical automation DevOps tool for IT orchestration. Ansible is an open-source tool by Red Hat.It helps to configure, provision, deploy and manage your system infrastructure across without facing any hassle. If you're attempting to migrate an older Docker-based AWX installation, see: Migrating Data from Local Docker The AWX Operator Starting in version 18.0, the AWX Operator is the preferred way to install AWX.
Ansible Tower (formerly ‘AWX’) is a web-based solution that makes Ansible even more easy to use for IT teams of all kinds. It’s designed to be the hub for all of your automation tasks.
Tower allows you to control access to who can access what, even allowing sharing of SSH credentials without someone being able to transfer those credentials. Inventory can be graphically managed or synced with a wide variety of cloud sources. It logs all of your jobs, integrates well with LDAP, and has an amazing browsable REST API. Command line tools are available for easy integration with Jenkins as well. Provisioning callbacks provide great support for autoscaling topologies.
AWX provides a web-based user interface, REST API, and task engine built on top of Ansible. It is the upstream project for Tower, a commercial derivative of AWX.
Prerequisites
Before you can run a deployment, you’ll need the following installed in your local environment:
- Ansible Requires Version 2.8+
- Docker
- A recent version
- docker Python module
- This is incompatible with
docker-py. If you have previously installeddocker-py, please uninstall it. - We use this module instead of
docker-pybecause it is what thedocker-composePython module requires.
- This is incompatible with
- Git Requires Version 1.8.4+
- Python 3.6+
- Node 10.x LTS version
- This is only required if you’re building your own container images with
use_container_for_build=false
- This is only required if you’re building your own container images with
- NPM 6.x LTS
- This is only required if you’re building your own container images with
use_container_for_build=false
- This is only required if you’re building your own container images with
System Requirements
The system that runs the AWX service will need to satisfy the following requirements
- At least 4GB of memory
- At least 2 cpu cores
- At least 20GB of space
- Running Docker, Openshift, or Kubernetes
- If you choose to use an external PostgreSQL database, please note that the minimum version is 10+.
Installation steps:
1. Install Dependencies
yum install -y epel-release
yum remove python-docker-py
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 ansible git python-devel python-pip python-docker-py vim-enhanced
pip install cryptography
pip install jsonschema
pip install docker-compose~=1.23.0
pip install docker –upgrade
2. Install docker
Configure docker ce stable repository.
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Installing docker.
yum install docker-ce -y
Start docker service.
systemctl start docker
Enable docker service.
systemctl enable docker
3. Deploy AWX
Clone AWX repo
git clone https://github.com/ansible/awx.git
Clone commercial logos
cd awx/
git clone https://github.com/ansible/awx-logos.git
Configure AWX
cd installer/

$ vim inventory
awx_official=true
Deploy AWX
ansible-playbook -i inventory install.yml -vv
Check the status
docker ps -a
AWX is ready and can be accessed from the browser.
http://ipaddress:80/
the default username is “admin” and the password is “password”.
Final checks:
- verify whether the service is started or not with
ss -tlnp | grep 80 - make sure your firewall is open for port 80
- make sure your OS is using python 3.6+ and pip3
https://github.com/ansible/awx/blob/devel/INSTALL.md
These days, Ansible is a big buzzword in the IT industry. It is a radical automation DevOps tool for IT orchestration.
Ansible is an open-source tool by Red Hat. It helps to configure, provision, deploy and manage your system infrastructure across without facing any hassle.
Ansible is agentless and requires no extra software with it. It can connect via SSH, remote PowerShell, and with remote APIs. It also uses a human-readable language, YAML so that one can easily adapt Ansible.
You have everything you need for your system automation in a complete package through Ansible.
How to install Ansible on Linux
In this first article on Ansible, you’ll learn about installing Ansible on various Linux distributions.
Personally, I prefer to get system information before installing any kind of software. Download adobe zii. Because It may help you in many aspects for different versions of an operating system.
Installing Ansible on Ubuntu and other Debian-based Linux distributions
Ansible is normally found in the default repositories of Ubuntu and Debian. You can use the command below to install it:
If Ansible package cannot be found, you can add the project’s PPA (personal package archive) to your system. You can add Ansible PPA by using the following command:

As you have added a new software source, you have to update your system to get packages available in the PPA. Update the software repositories list with this command:
Finally, you can install Ansible using this command:
After successful completion of the above command, Ansible will be installed on your system.
You should verify the installation by checking the version of Ansible you just installed:
Ansible Docker Install Centos
Installing Ansible on CentOS, Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE etc
To install the latest version on Ansible in CentOS , you should install EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) first using the below command:
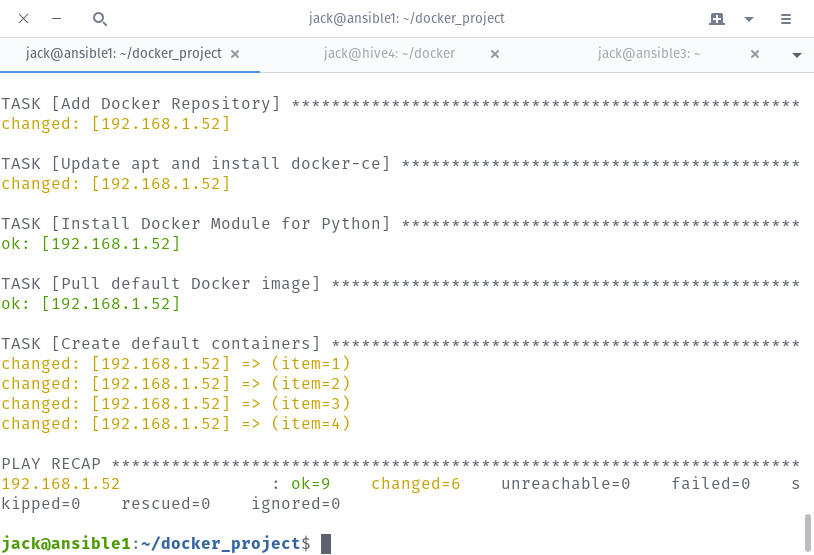
Then you can easily install Ansible using this command:
You can check Ansible version using this command:
and its output
How to uninstall Ansible
If you want to uninstall Ansible for some reasons, you can easily do that.
Uninstall Ansible from Ubuntu/Debian
You can uninstall or remove Ansible from Ubuntu. Use this command:
But if you want to remove Ansible along with its all dependency packages. Use this command:
.png)
Uninstall Ansible from CentOS/Red Hat
You can uninstall or remove Ansible from CentOS using this command:
In the next article, I will cover how to connect and access several machines through SSH connection establishment using Ansible. Stay tuned for the Ansible tutorial series.
Docker Hub
Become a Member for FREE
Ansible Docker Install Plugin
Join the conversation.
